跨域
什么是跨域
跨域,指的是浏览器不能执行其他网站的脚本。它是由浏览器的同源策略造成的,是浏览器施加的安全限制。
所谓同源是指,域名,协议,端口均相同,不明白没关系,举个栗子:
你的服务URL是 localhost:12345, 当你再这个URL的界面js文件里访问 localhost:12346 的地址时,会被禁止,该问题为跨域问题。
我们用代码来实现跨域:
后端代码:
// URL localhost:8888/cross
@RestController
public class CrossDomainController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/cross", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getHelloWorld() {
return "hello world";
}
}
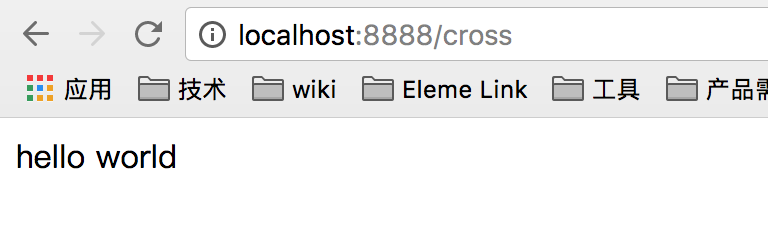
在浏览器输入 localhost:8888/cross 结果如下:
前端代码:
<template>
<h1></h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'hello'
}
},
created: function() {
this.$http.get('http://localhost:8888/cross').then(function(response){
console.log(response)
this.msg = response.bodyText
}, function(response){
this.msg = 'get Error'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
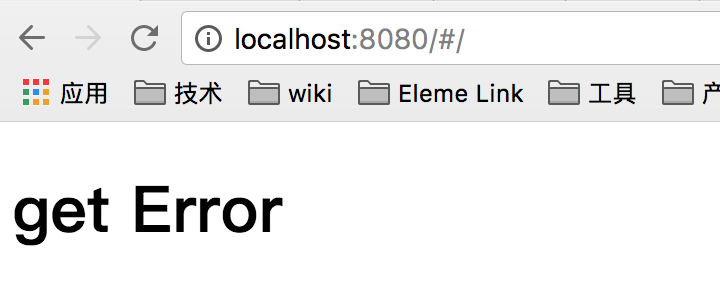
我们跑一下结果如下:
然后来看下 control:
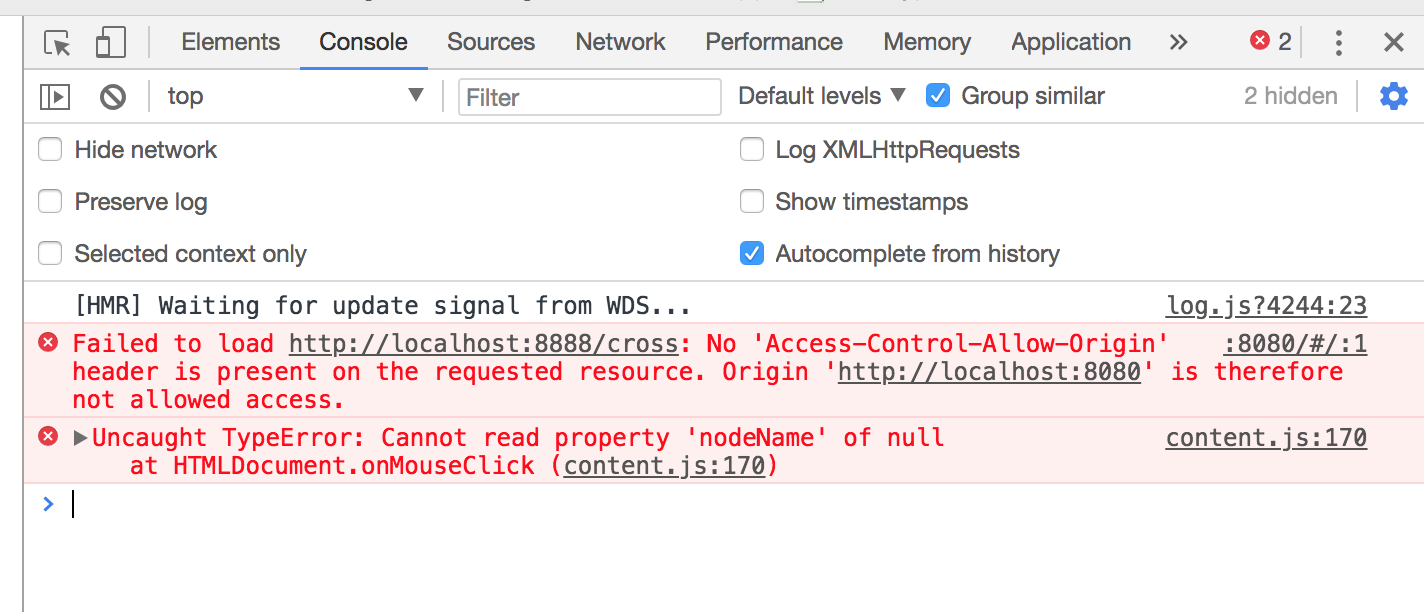
Failed to load http://localhost:8888/cross: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. Origin 'http://localhost:8080' is therefore not allowed access 的意思大致是 http://localhost:8888/cross加载失败, 因为在 请求http://localhost:8888/cross的返回头里面没有 Access-Control-Allow-Origin, 所以 http://localhost:8080 的访问被拒绝
为什么会有跨域
发生跨域问题大概有三个原因:
浏览器限制
其实跨域问题是浏览器做的限制,而不是服务器后台的限制, 当浏览器发现请求是跨域的,就会去校验跨域请求的返回值里面是否有一些允许跨域的标示, 如果没有这些标示,则浏览器报跨域异常。
跨域
这个就是说 当你请求的地址 跟你当前的地址 有 ip/端口/协议 有任何一个不一样,就会发生跨域。
XHR请求
当请求是XHR(XmlHttpRequest)的时候, 浏览器就会去判断是否跨域。 这个很好验证,比如在localhost:8080界面中使用 <a href="localhost:8888/cross"> 标签,并不会被浏览器识别跨域。
怎么解决跨域
解决思路也是根据产生的原因去找对应的策略:
如何从解决浏览器限制
浏览器制定启动参数
在打开浏览器的时候 可以增加一个参数 --disable-web-security
open -n Google\ Chrome.app/ --args --disable-web-security --user-data-dir=随便一个目录
打开之后的效果如下:
我们再看看之前的页面请求:
我们发现 跨域问题已经没有了, 不过这不是一个常用的解决办法。
不发出XHR请求
JsonP
JsonP 是什么?
jsonP 是 json的一个扩展, 主要是使用javascript脚本代替xhr请求来解决跨域
jsonP 服务后台代码也是要修改的
我们修改一下前台的代码:
<template>
<h1></h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'hello'
}
},
created: function() {
this.$http.jsonp('http://localhost:8888/cross').then(function(response){
console.log(response)
this.msg = response.bodyText
}, function(response){
this.msg = 'get Error'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
看下请求结果:
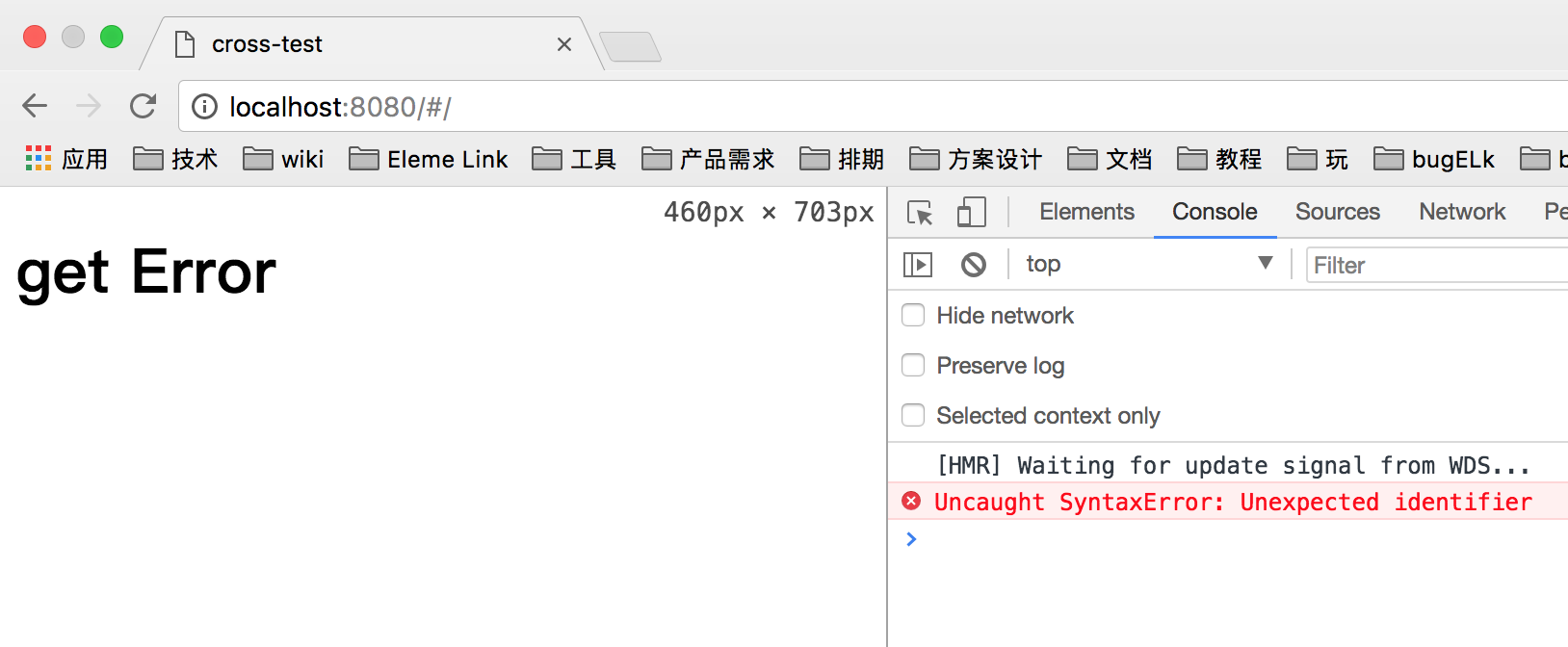
我们发现浏览器报错换了, 为什么这样呢? 因为jsonP请求会将返回体当作一段js代码来使用, 我们后段返回 hello world 并不是js的语法,所以前端解析失败, 所以使用jsonp要对后段代码进行改动, 我们改成如下代码:
@RestController
public class CrossDomainController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/cross", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getHelloWorld() {
return "hello world";
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/cross/bean", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseBean getHelloWorldBean() {
return new ResponseBean() ;
}
}
@Data
public class ResponseBean {
private String data;
}
@ControllerAdvice
public class JsonPAdvice extends AbstractJsonpResponseBodyAdvice {
public JsonPAdvice() {
super("callback");
}
}
<template>
<h1></h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'hello'
}
},
created: function() {
this.$http.jsonp('http://localhost:8888/cross/bean').then(function(response){
console.log(response)
this.msg = response.body.data
}, function(response){
this.msg = 'get Error'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
先说一下, 为什么要使用/cross/bean 因为jsonp返回的东西,浏览器当成javascript脚本来使用, /cross返回的 hello world 不符合js的语法,所以不能正常运行。
我们看下运行结果
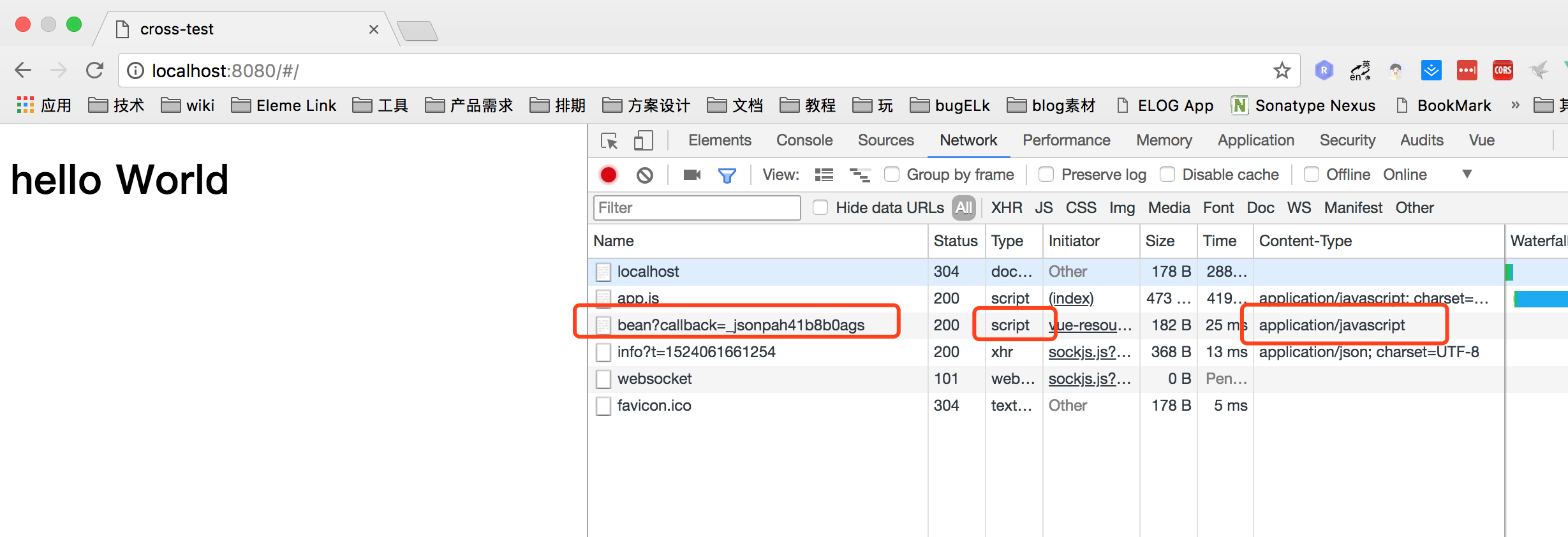
我们发现, response 不再是json类型, request 也不在时xhr类型, 所以证明 jsonp只是将后端返回当成javascript脚本来运行
JsonP 的弊端
- 服务器需要改动代码
如果服务器端不是自己的, 就没有办法改动服务器代码
- 只支持GET方法
因为是通过动态创建script脚本来发送请求, 所以除了GET方法,其他的都不支持。
- 发出去的不是XHR请求
这也是jsonP为什么可以解决跨域的根本原因, 不能使用XHR一些特性
解决跨域
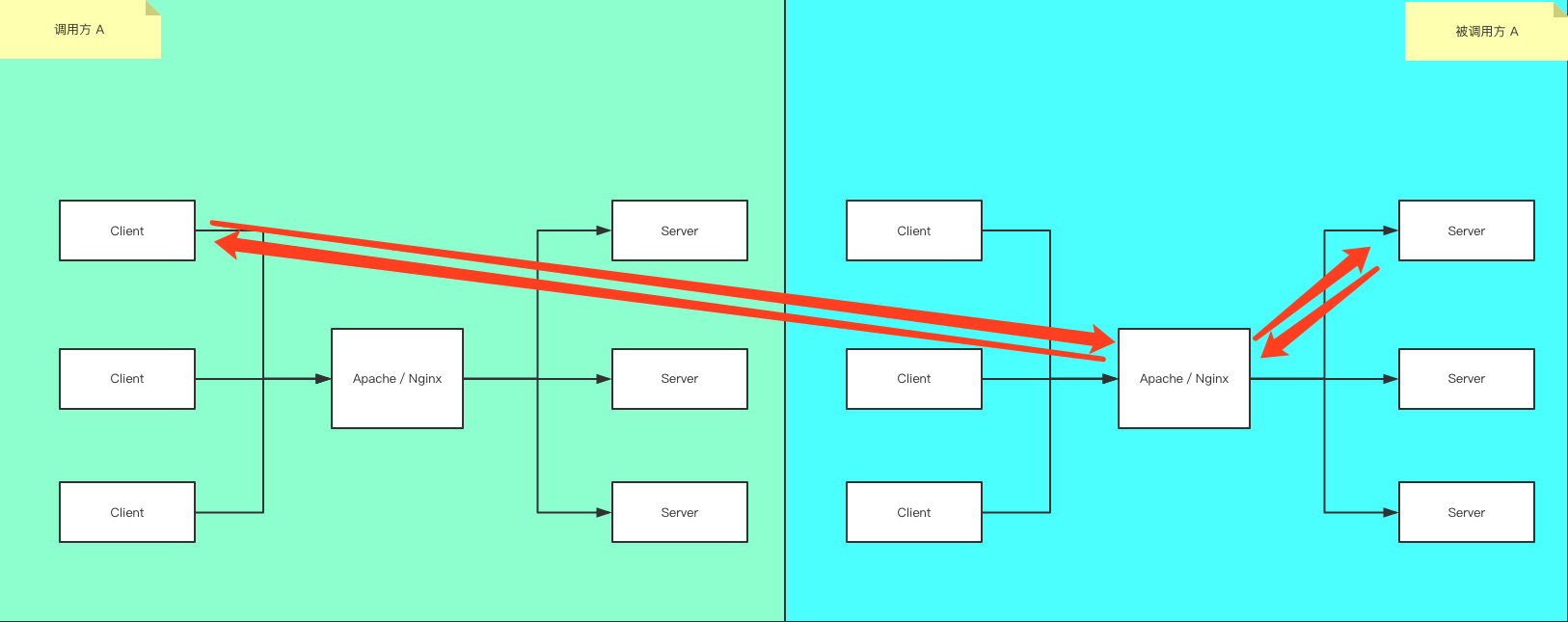
常用的BS架构
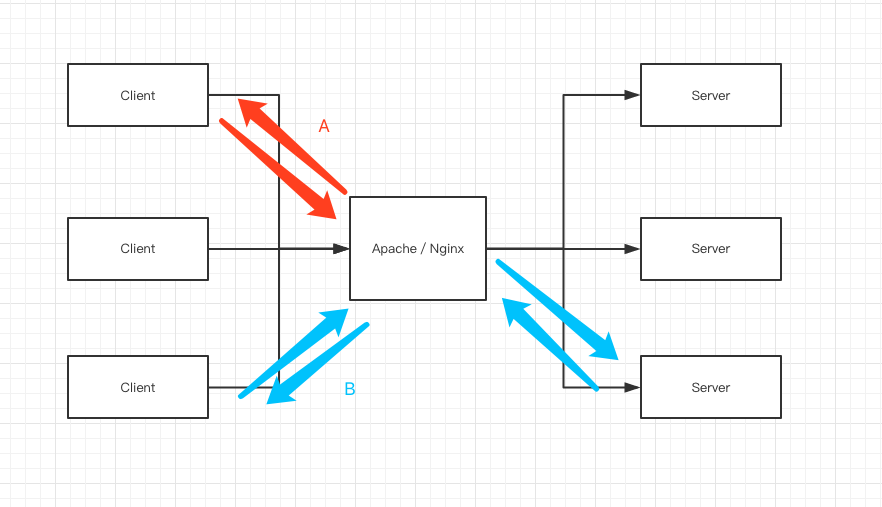
我们常用的Browser/Server 架构如图所示, Browser 端发起请求 到 中间服务器(Apache or Nginx), 中间服务器判断该请求是请求静态资源,还是请求动态资源? 如果是请求静态资源,则走A链路, 如果请求动态资源则走B链路。
- A链路: 如html, css, js, img 等这些静态资源
- B链路: 如post,get,delete 这些请求
BS架构,跨域
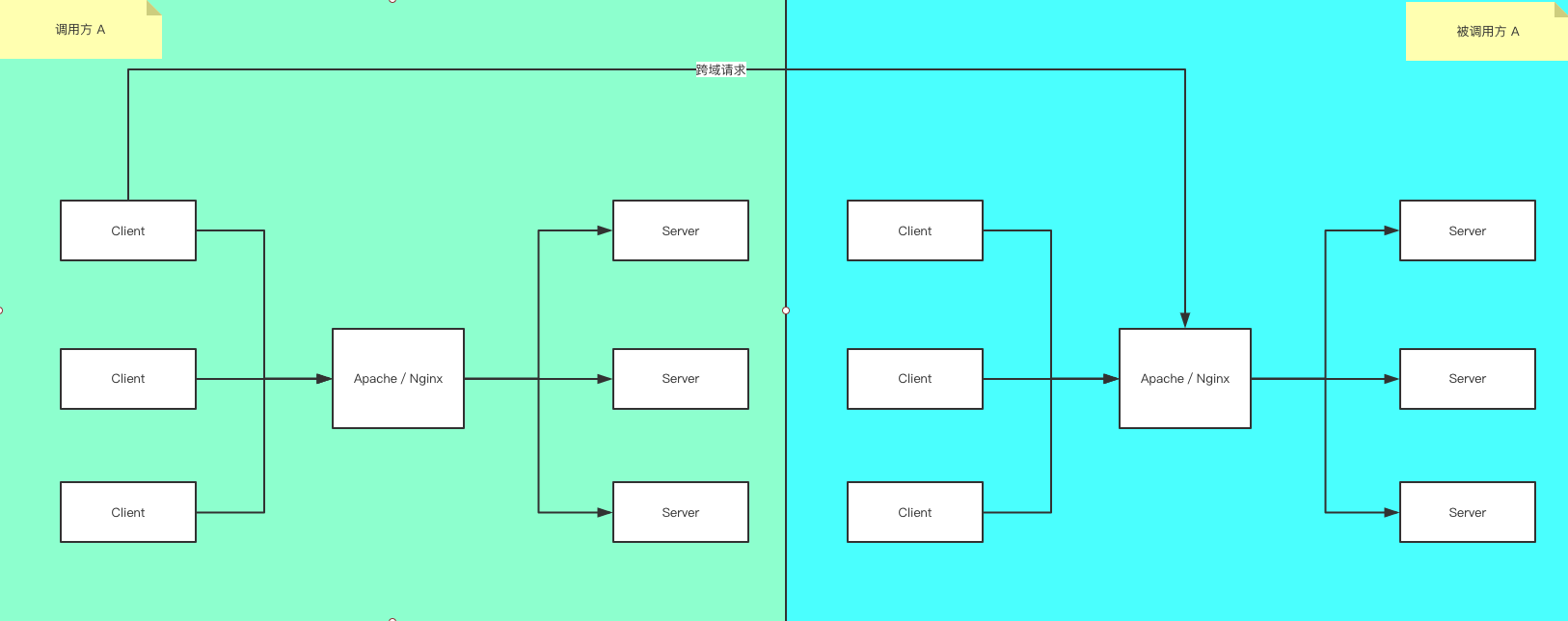
如图所示, 当调用方A在Browser(浏览器)端请求 被调用方B的时候,就会发生跨域问题, 那么如何解决呢?
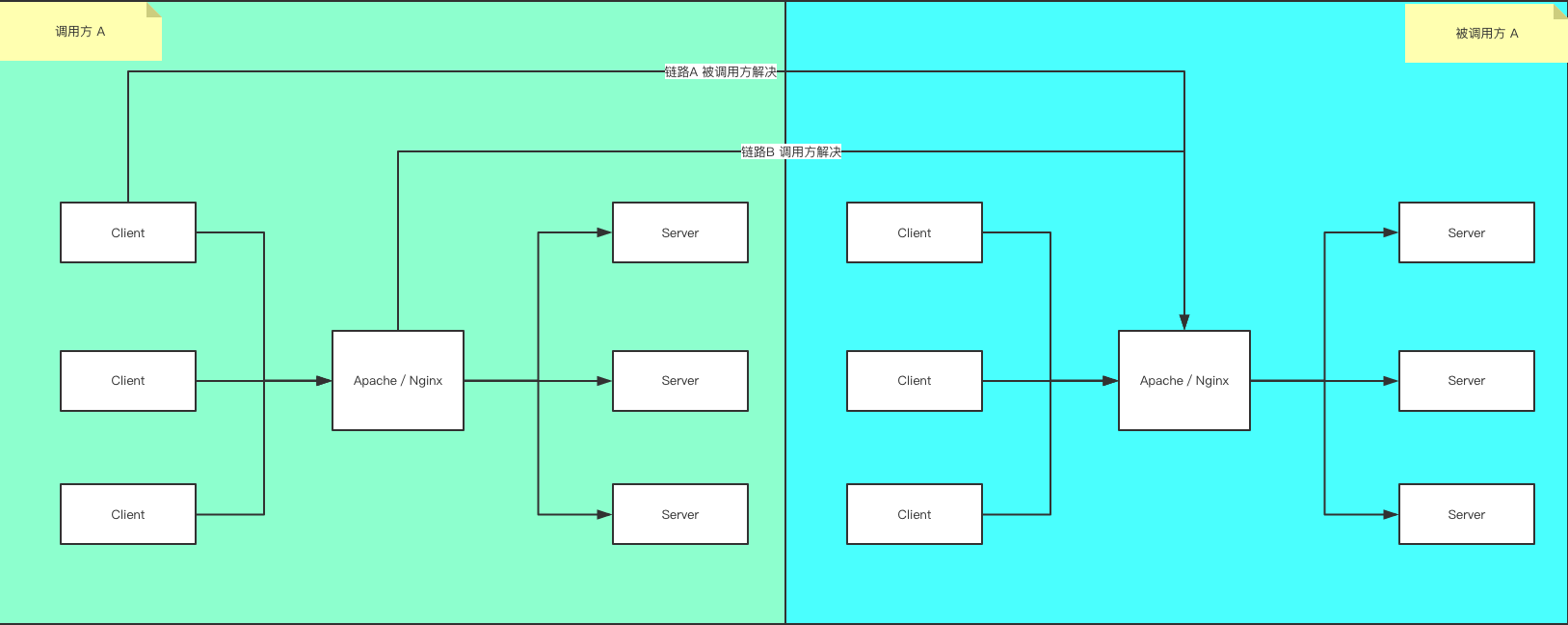
有两种解决方法:
- 修改被调用方,使其在header里面返回一些标示,来标记该服务支持跨域
- 修改调用方,使用Apache/Nginx的一些配置,让浏览器请求Apache/Nginx,由Apache/Nginx转发到被调用方B的请求,让浏览器感觉不到跨域。
好,接下来我们一个一个的实现
调用方修改
调用方解决方案 就是当没有办法修改被调用方的服务器代码时,就要在调用方请求处想办法解决跨域, 可以使用反向代理方式。
反向代理
反向代理(Reverse Proxy)方式是指以代理服务器来接受internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器,并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给internet上请求连接的客户端,此时代理服务器对外就表现为一个反向代理服务器。
说白了,就是 浏览器访问同一个url上的不同地址, 如 localhost:8080/A, localhost:8080/B, 然后反向代理服务器可以把请求链接代理到不同地址的服务器上 ,如Nginx把 localhost:8080/B 代理到 localhost:8081 上, 浏览器 感觉不出来跨域, 也就是隐藏跨域。
Nginx 配置
我们先把 前后端代码改成不能跨域的
public class CrossFilter implements javax.servlet.Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
<template>
<h1></h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'hello'
}
},
created: function() {
this.$http.post('http://localhost:8888/cross/bean', JSON.stringify({data: "gc"})).then(function(response){
console.log(response)
this.msg = response.body.data
}, function(response){
this.msg = 'get Error'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
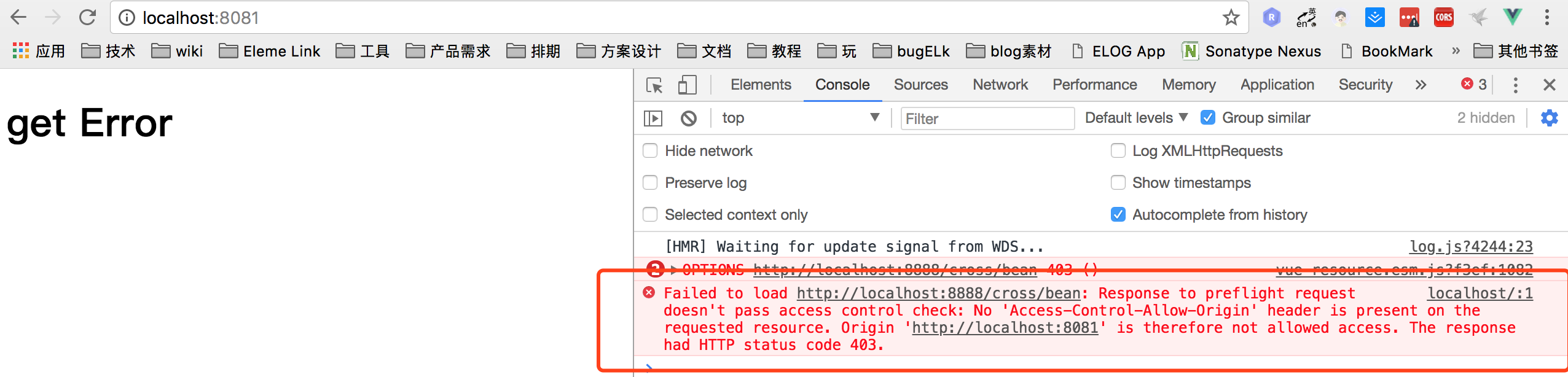
我们看 现在是不允许跨域的, 现在我们配置下nginx:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8081;
}
location /ajaxserver{
proxy_pass http://localhost:8888/cross/bean;
}
}
看这个nginx的配置, 我们把 localhost 路由到 http://localhost:8081 路径上, 我们把 localhost/ajaxserver 路由到 http://localhost:8888/cross/bean, 然后我们再改下 前端请求的路径:
<template>
<h1></h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'hello'
}
},
created: function() {
this.$http.post('/ajaxserver', JSON.stringify({data: "gc"})).then(function(response){
console.log(response)
this.msg = response.body.data
}, function(response){
this.msg = 'get Error'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
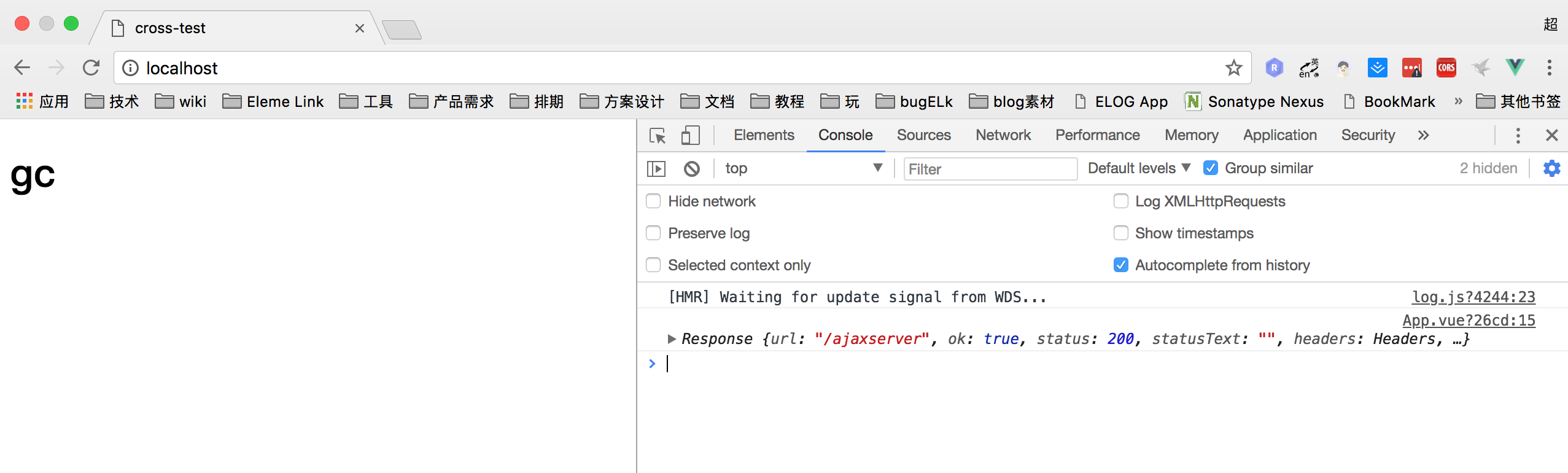
我们看,浏览器已经不显示跨域了。 这样 我们成功的对浏览器隐藏了跨域。
被调用方修改
实现代码
被调用方修改,就是在请求的响应头中增加一些标示,让浏览器允许跨域, 可以修改相应头的地方有两处, 这里只介绍在后端代码里如何修改响应头, Apache/Nginx 服务器上修改的方法,本文不做演示
@ComponentScan("me.int32")
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean registerFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.addUrlPatterns("*");
bean.setFilter(new CrossFilter());
return bean;
}
}
package me.int32.filter;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CrossFilter implements javax.servlet.Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
resp.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
resp.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "*");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
<template>
<h1></h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'hello'
}
},
created: function() {
this.$http.get('http://localhost:8888/cross/bean').then(function(response){
console.log(response)
this.msg = response.body.data
}, function(response){
this.msg = 'get Error'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
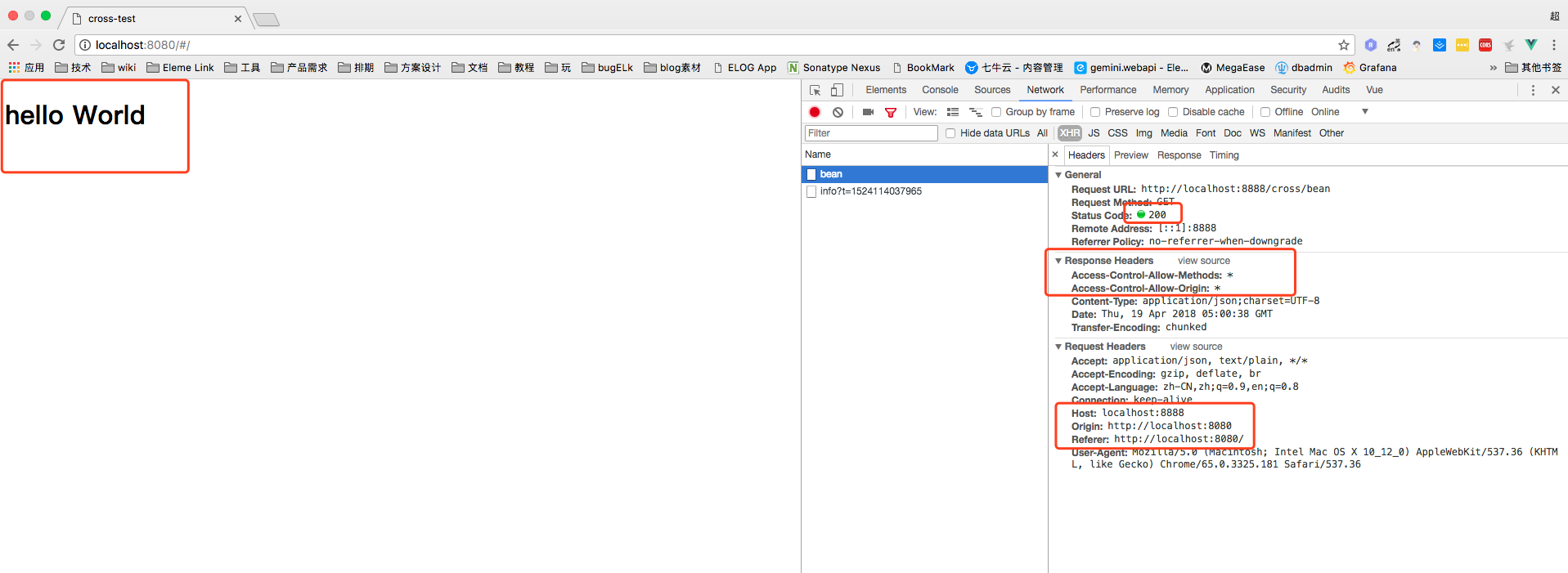
可以看到Response Header 里面带了 Access-Control-Allow-Methods:* 和 Access-Control-Allow-Origin:* 两个标示, 代表着, 允许浏览器对所有源,所有方法进行跨域请求.
先判断,后执行
浏览器的请求并不都是先执行后判断,即先请求服务接口, 根据服务接口的响应头去判断是否允许跨域, 也有一些请求是先发一个预处理请求,这个预处理请求就包括判断是否跨域, 如果允许跨域,才会发送真正的请求。
哪些是需要发预处理请求(复杂请求),哪些是不需要(简单请求)的呢? 我们可以这样区分:
- 简单请求:
- GET,POST,HEAD 方法中的一种
- 无自定义头
- Content-Type in [text/plain, multipart/form-data, appliocation/x-www-form-urlencoded]
- 复杂请求:
- PUT, DELETE 方法的ajax请求
- 发送json格式的 ajax 请求
- 带自定义头的 ajax 请求
我们来发送一个复杂请求:
@RestController
public class CrossDomainController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/cross", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getHelloWorld() {
return "hello world";
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/cross/bean", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseBean getHelloWorldBean() {
return new ResponseBean() ;
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/cross/bean", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseBean getRequestBean(@RequestBody RequestBean requestBean) {
System.out.println(".....");
return new ResponseBean() ;
}
}
<template>
<h1></h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'hello'
}
},
created: function() {
this.$http.post('http://localhost:8888/cross/bean', JSON.stringify({data: "gc"})).then(function(response){
console.log(response)
this.msg = response.body.data
}, function(response){
this.msg = 'get Error'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
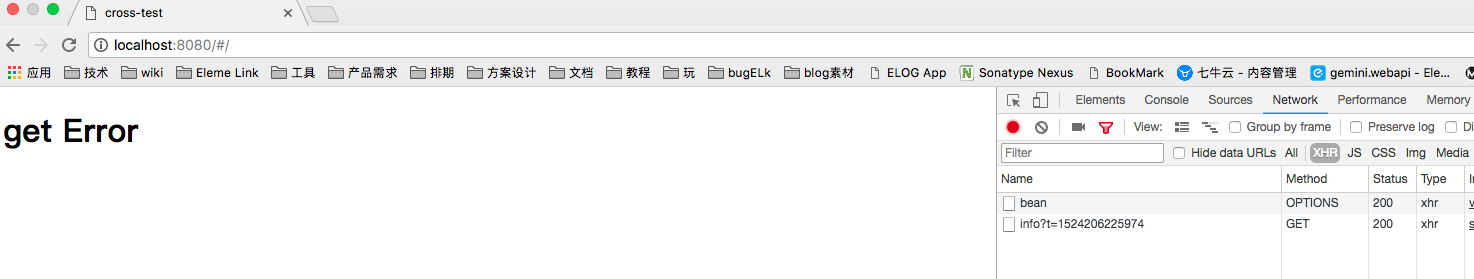
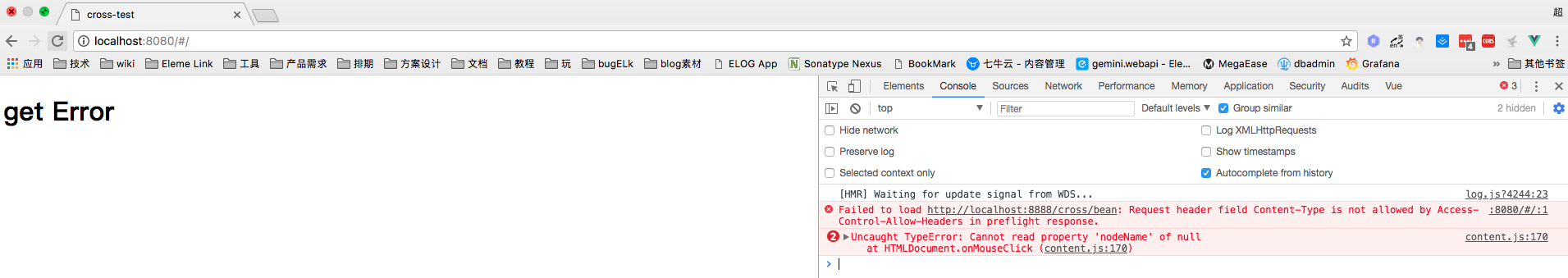
我们看下, 这种ajax json post 请求,并不单单是发送一个post, 而是先发送一个 method=OPETION 的预检请求, 但是由于预检请求没有被通过 : 我们看到 前端需要后端回给一个 Access-Control-Allow-Headers:Content-Type , 我们修改下后端代码:
public class CrossFilter implements javax.servlet.Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
resp.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
resp.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "*");
resp.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
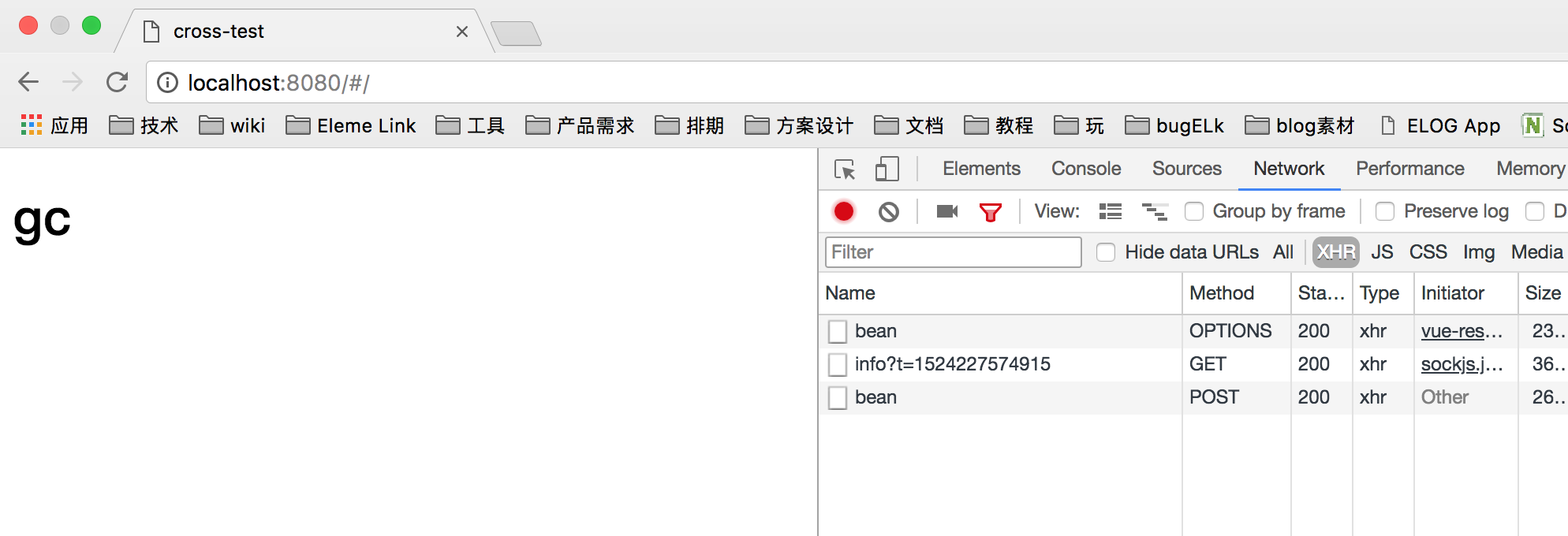
我们看到,请求已经成功了 … 在这里,我们也看到了所谓的预检请求 OPETION 。 但是 每次请求都去做一次 预检请求 比较浪费流量,影响效率, 我们可以在相应头中增加 Access-Control-Max-Age:3600 来设置Opetion操作的缓存时间, 这样在缓存生效时间内就不需要再次进行Opetion请求了。
* 不是万能的
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:* 并不是万能的, 当请求携带cookie的时候, 浏览器是不允许 使用* 通配符的, 所以当带cookie的时候,Access-Control-Allow-Origin 这个字段必须是全匹配的。 而且还需要增加一个 Access-Control-Allow-Credentials:true 这个相应头。
自定义请求头
当ajax 请求 带自定义请求头的时候,后端相应也必须带上相应的请求头, 不然仍然会出现 跨域异常
总结
我们从 为什么会解决跨域 到 根据跨域产生的原因解决跨域 阐述了跨域 和 解决办法, 这样在我们平时再遇到跨域的时候就可以变得更加从容, 如果 调用方 和 被调用方 都是你自己, 可以选择 被调用方解决跨域, 修改下服务器的代码即可。 如果你是调用方, 被调用方是别人, 那么 可以使用 nginx 对跨域进行隐藏。